Imaging and Management of Myeloma Bone Disease
Poster Session 1
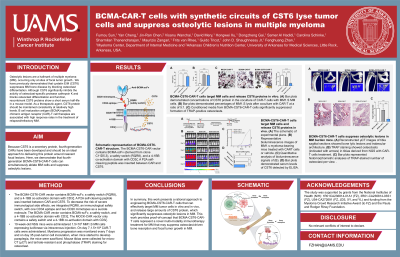
P-066: BCMA-CAR-T cells with synthetic circuits of CST6 lyse tumor cells and suppress osteolytic lesions in multiple myeloma
Wednesday, September 27, 2023
1:30 PM - 2:30 PM EEST

Fanghuang Zhan, MD & PhD (he/him/his)
Professor
University of Arkasas Medical Sciences
Little Rock, Arkansas, United States
Introduction: Osteolytic lesions are a hallmark of multiple myeloma (MM). We have previously demonstrated that cystatin E/M (CST6) suppresses MM bone disease by blocking osteoclast differentiation. Recombinant CST6 protein has a short serum half-life in a mouse model. As a therapeutic agent, CST6 protein concentrations should be maintained at relatively high levels. B cell maturation antigen (BCMA)-specific chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapies are associated with high response rates in the treatment of MM. Fourth-generation CARs have been developed and are ideal to deliver CST6, which is a secretory protein, close to nascent focal lesions. Here, we demonstrate that BCMA-CST6-CAR-T cells simultaneously ablate MM cells and suppress osteolytic lesions.
Methods: The BCMA-CST6-CAR vector contains BCMA-scFv and a 4-1BB co-activation domain with CD3ζ. A P2A self-cleaving peptide was inserted between CAR and CST6. CAR-T cells were incubated with MM1.S cells at a ratio of 5:1 for 24 h. To evaluate the in vivo anti-tumor activity and anti-bone resorption of BCMA-CST6-CAR-T cells, we injected MM1.S cells expressing luciferase into NSG mice. On day 7, MM-bearing mice received CAR-T cells. These mice were sacrificed on day 35, mouse serum CST6 concentrations were evaluated by ELISA, and mouse tibiae were collected for μCT and TRAP staining.
Results: The percentage of lysed MM1.S cells was 77.2% after 24 h co-culturing with CAR-T cells. No difference in killing was observed between BCMA-CAR-T group and BCMA-CST6-CAR-T group. T cell activation marker CD69 was significantly increased in BCMA-CST6-CAR-T (70.9%) group compared to the MOCK-CAR-T group (9.2%). Bioluminescence imaging of MM-bearing mice revealed that BCMA-CST6-CAR-T cells affected excellent antitumor activity, yielding near-complete tumor clearance by day 21. Again, BCMA-CST6-CAR-T cells and BCAM-CAR-T cells showed very similar effects on inhibiting tumor growth. CST6 serum concentration was significantly higher in the BCAM-CST6-CAR-T group (938.4 ng/ml) compared to the MOCK group (60.9 ng/ml) and BCMA-CAR-T group (64.2 ng/ml) (P < 0.001), indicating that BCMA-CST6-CAR-T cells secrete high levels of CST6 protein in vivo. μCT images of mouse tibiae showed that BCMA-CST6-CAR-T cells significantly suppressed osteolytic lesions in MM-bearing mice. TRAP staining of mouse tibia sections demonstrated that the BCMA-CST6-CAR-T cells significantly reduced osteoclast numbers and the proportion of bone surface occupied by osteoclasts.
Conclusions: This work presents a rational approach to engineering BCMA-CST6-CAR-T cells that can effectively target MM cells and release large amounts of CST6 protein, which efficiently suppresses osteolytic lesions in MM.
Methods: The BCMA-CST6-CAR vector contains BCMA-scFv and a 4-1BB co-activation domain with CD3ζ. A P2A self-cleaving peptide was inserted between CAR and CST6. CAR-T cells were incubated with MM1.S cells at a ratio of 5:1 for 24 h. To evaluate the in vivo anti-tumor activity and anti-bone resorption of BCMA-CST6-CAR-T cells, we injected MM1.S cells expressing luciferase into NSG mice. On day 7, MM-bearing mice received CAR-T cells. These mice were sacrificed on day 35, mouse serum CST6 concentrations were evaluated by ELISA, and mouse tibiae were collected for μCT and TRAP staining.
Results: The percentage of lysed MM1.S cells was 77.2% after 24 h co-culturing with CAR-T cells. No difference in killing was observed between BCMA-CAR-T group and BCMA-CST6-CAR-T group. T cell activation marker CD69 was significantly increased in BCMA-CST6-CAR-T (70.9%) group compared to the MOCK-CAR-T group (9.2%). Bioluminescence imaging of MM-bearing mice revealed that BCMA-CST6-CAR-T cells affected excellent antitumor activity, yielding near-complete tumor clearance by day 21. Again, BCMA-CST6-CAR-T cells and BCAM-CAR-T cells showed very similar effects on inhibiting tumor growth. CST6 serum concentration was significantly higher in the BCAM-CST6-CAR-T group (938.4 ng/ml) compared to the MOCK group (60.9 ng/ml) and BCMA-CAR-T group (64.2 ng/ml) (P < 0.001), indicating that BCMA-CST6-CAR-T cells secrete high levels of CST6 protein in vivo. μCT images of mouse tibiae showed that BCMA-CST6-CAR-T cells significantly suppressed osteolytic lesions in MM-bearing mice. TRAP staining of mouse tibia sections demonstrated that the BCMA-CST6-CAR-T cells significantly reduced osteoclast numbers and the proportion of bone surface occupied by osteoclasts.
Conclusions: This work presents a rational approach to engineering BCMA-CST6-CAR-T cells that can effectively target MM cells and release large amounts of CST6 protein, which efficiently suppresses osteolytic lesions in MM.
